Chapter 10 Linguistics and Foreign Language Teaching
10.1 Foreign language teaching as a system
Linguistics plays its role in foreign language teaching. In order to understand the role of linguistics we need to sketch how foreign language teaching as a system operates. In China, foreign language teaching as a component of education is composed of activities on four levels. The first level is educational planning. The government decides what languages are taught, to whom, and what educational resources are provided. The decision is in accordance with the socio-economic needs of the society. The social aim or objective is clearly stated.
The second level is preparation. On this level, there are two parallel sets of activities. One is syllabus design and material development. The syllabus and the textbooks are prepared according to the social aim for teaching a language. They turn social aims into pedagogic objectives. The syllabus authoritatively decides what to teach and what principles guide the teaching and learning. These practices are guided by theories of relevant disciplines, such as linguistics, psychology, pedagogy, etc. These activities are the commitment of specialists. The other set of activities is teacher preparation and retraining. The two parallel sets of activities keep abreast of professional advancement. When new syllabi and textbooks come out following a new approach to language teaching, teachers have to be retrained in order to bring the new ideas into practice in the classroom.
The third level is operation in the classroom. There are three main variables that determine the outcome of teaching and learning --- the learners, the teacher, and the textbook. The learners' attitude toward the learning task and their motivation are strongly influenced by the social milieu. The teacher's view of language and language learning determine what he/she teaches and how. The textbook decides, to a great extent, the content of teaching, but what the students really learn also depends on what goes on in the classroom. Behind the teacher's practice and the textbook are certain theories of language and language acquisition.
The fourth level is evaluation, mostly in the form of testing. Educational administrators need to find out the efficiency of teaching and learning, as the cost is tremendous. Students need to be credited and selected. Therefore, language tests must be administered at various levels of education. Language testing is a complex activity which is guided by linguistic and psychological theories.
The whole system of foreign language teaching can be represented by a conceptual framework below. As shown by the figure, linguistics and other relevant disciplines contribute to the levels of preparation, operation and evaluation. The rest of this chapter will survey the contribution of linguistics to foreign language teaching.
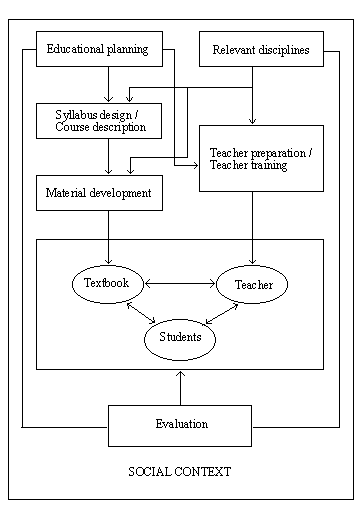
A conceptual framework of foreign language teaching as a system